OTHER CHARACTERISTICS
OTHER CHARACTERISTICS OF THE JHR
Seismic pads
To protect the JHR Material Test Reactor against seismic risks present in the area required a specific design for the nuclear unit. It rests on two concrete slabs separated by 198 seismic pads (concrete blocks and elastomer absorbers), which can maintain full integrity of the building in the event of a major earthquake.
The JHR Material Test Reactor rests on seismic pads specifically designed to uncouple building movements from ground movements. This technique is well known in bridge construction and has already been applied on other nuclear plants.
The seismic pads can be described as ‘sandwiches’ measuring 40 cm by 40 cm, consisting of six layers of 2 cm-thick rubber (elastomer supports) inserted into metal plates, at a rate of 1 or 2 support elements per pad.
Placed at the top of 2.2 m-high concrete columns rising from the lower part of the structure’s floor, these pads support the upper floor – the ‘raft’ – which is the true ‘floor’ of the facility.
Each pad supports a load of 550 tonnes. They are arranged so that the total load of the facility (110,000 tonnes) is uniformly distributed over the structure.

Seismic pads
© CEA/LESENECHAL GERARD
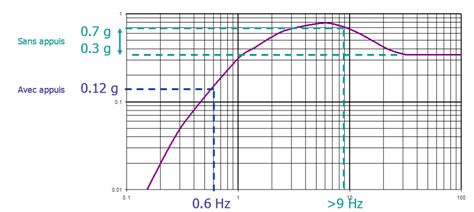
These seismic pads are the key to ‘seismic base isolation’.
Their flexible structure is able to dilute the effects of shaking, vibrations or more specifically the accelerations caused by a strong earthquake. In other words, the seismic pads can reduce the horizontal acceleration experienced by the nuclear unit in the event of a design-basis earthquake. This system is simple, strong and requires little maintenance.
Pre-stressed cables
Pre-stressed cables were used to build the JHR Material Test Reactor to reinforce the facility’s assembly.
A pre-stressed cableis made of a duct filled with sheathed greased strands. The strands have a cross section of 15 mm2 and are composed of 7 twisted wires.

The following pre-stressed cabling was used:
– 20 purely vertical cables anchored in the wall of the dome and composed of 15 strands
– 60 gamma cables run vertically then turned on the dome and anchored to the dome wall, composed of 14 strands
– 25 horizontal cables from level 0 up to the dome wall and composed of 11 strands
– 16 purely dome cables anchored to the dome wall and comprising 14 strands, i.e. a linear length of 8.5 km of duct and a linear strand length of 111 km.



